程序的机器级表示 1
程序的机器级表示 1
History of Intel processors and architectures
本书只研究 x86-64 架构的问题。
> gcc -m64 hello.cC, Assembly, Machine code
代码格式:
- Assembly Code(汇编代码): A text representation of machine code.
- Object Code(目标代码): 和 Machine Code 差不多,只是少了 link 过程。
- Machine Code(机器代码): The byte-level programs that a processor executes
下面这个由 c 语言转换到机器语言的图展示了这三种语言的关系:
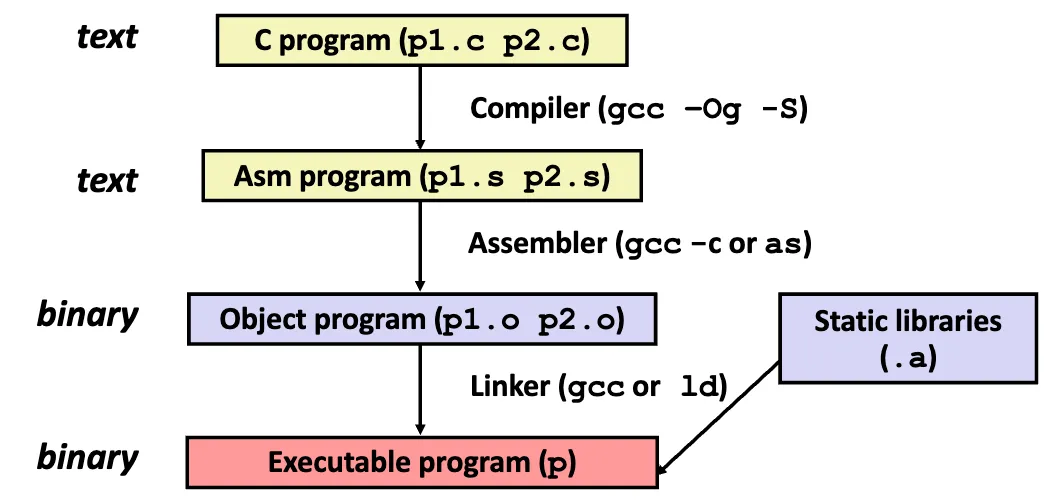
Assembly code
下面的指令可以利用生成后缀名为 .s 的汇编文件。
gcc -Og -S mstore.c # 生成汇编文件mstore.s其中 -Og 是一个适用于调试的优化选项,确保生成的调试信息不会受到影响。
数据类型:
| C语言 | Intel数据类型 | 汇编后缀 | 字节数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| char | Byte | b | 1 |
| short | Word | w | 2 |
| int | Double word | l | 4 |
| long | Quad word | q | 8 |
| char * | Quad word | q | 8 |
| float | Single precision | s | 4 |
| double | Double precision | l | 8 |
操作:
是在 Register / Memory 的数据上进行操作:运算、传送数据(Transfer data)、控制转移(Transfer control)。
Object Code
在 Assembler(汇编器)与 Linker(连接器)之间。
汇编器的功能:
- .s文件汇编为.o文件
- 指令的二进制编码,几乎是可执行的,只差链接过程
下面的指令可以利用生成后缀名为 .s 的汇编文件。
gcc -Og -c mstore.c # 生成目标代码文件mstore.o这是二进制格式,无法直接查看,需要反汇编工具:
objdump -d mstore.o来检查 object code,得到与汇编大致对应的代码,以分析指令序列。
Assembly Basics: Registers, operands, move
寄存器、操作数(运算对象)、数据传送指令。
传送数据
首先以 movq 的一个示例来介绍。
Instruction: 指令,由操作码(Operation Code)和操作数(Operands)组成。比如下面是用于 Moving Data 的指令:
其中 和 就是操作数。
Operand: 操作数有以下类型:
- Immediate: const integer data. 比如:$0x400, $533,在前面加个 $ 即可。
- Register: One of 16 integer registers. 共有十六个寄存器,例如 .
- Memory Reference: 8 consecutive bytes of memory at address given by register. 寄存器后的连续八个字节,记作 ,加个括号。
在 指令中,这三者都可以被组合起来,有如下用法:

注意不存在 mem 到 mem 的操作。
完整寻址模式
- :长偏移量,1、2、4 字节
- :基址寄存器,16个整型寄存器中的任意一个
- :索引寄存器,除 %rsp 外的任一寄存器
- :伸缩值,1,2,4 或 8
这样可以计算出一个地址,然后进行数据传送。
Arithmetic & logical operations
算数与运算逻辑操作。
地址计算指令
利用寻址模式表达式,可以进行:
- 计算地址但不存储,
- 计算形如 的算数表达式。
这里用到的就是第二种功能,计算算数表达式,例如:
long m12(long x) {
return x*12;
}转换为汇编语言为:
leaq (%rdi,%rdi,2), %rax
salq $2, %rax其中 是寻址模式表达式,计算 ,
然后 是左移两位,即 。
Arithmetic Operations
一些算数操作,包括二元运算和一元运算,这里不进行列举。
在汇编层面,已经不区分有符号数和无符号数的运算,都是对二进制码的操作。
二元运算中,以 为例,表示 ,要注意参数的顺序。
例子:
long arith(long x, long y, long z) {
long t1 = x + y;
long t2 = z + t1;
long t3 = x + 4;
long t4 = y * 48;
long t5 = t3 + t4;
long rval = t2 * t5;
return rval;
}其汇编代码为:
arith:
leaq (%rdi,%rsi), %rax # t1 = x + y
addq %rdx, %rax # t2 = z + t1
leaq (%rsi,%rsi,2), %rdx # for t4
salq $4, %rdx # t4 = y * 48
leaq 4(%rdi,%rdx), %rcx # t5 = t3 + t4
imulq %rcx, %rax # rval = t2 * t5
ret这里寄存器与参数的对应关系为:
| 寄存器 | 参数 |
|---|---|
注意寄存器的重复使用,以及编译器没有显式计算 的值,以节省寄存器。
Waiting for api.github.com...